C++でライフゲームを実装する
お勉強のためC++でライフゲームを実装してみます。
ルールや実行イメージは以下のページのシミュレータで確認できます。
ライフゲームとは
ライフゲームとは、4つのルールから生命の誕生や進化、淘汰をシミュレーションできるゲームです。ライフゲームを観察することで、いくつかのパターンを見つけたりすることができます。
セル(細胞)が2次元の格子状に配置されていて、各セルには8つの近傍のセルがあります。セルは生きた状態と死んだ状態のいずれかです。
以下の4つのルールで次世代のセルの状態が決められます。
- 誕生:死んでいるセルに隣接する生きたセルがちょうど3つあれば、次の世代が誕生する。
- 生存:生きているセルに隣接する生きたセルが2つか3つならば、次の世代でも生存する。
- 過疎:生きているセルに隣接する生きたセルが1つ以下ならば、過疎により死滅する。
- 過密:生きているセルに隣接する生きたセルが4つ以上ならば、過密により死滅する。
ということで実装します。
実装コード
#include <algorithm>
#include <iostream>
#include <thread>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
struct LifeGame {
vector<vector<bool>> data;
vector<vector<bool>> next;
int width;
int height;
LifeGame(int w, int h) {
width = w;
height = h;
data = vector<vector<bool>>(height, vector<bool>(width, 0));
}
public:
void start() {
display();
while (true) {
// 0.5秒待
std::this_thread::sleep_for(std::chrono::milliseconds(500));
// 状態の更新
update();
// 描画
display();
}
}
private:
void update() {
// 次世代の状態
next = vector<vector<bool>>(height, vector<bool>(width, 0));
for (int y = 0; y < height; y++) {
for (int x = 0; x < width; x++) {
// 現在のセルの状態
bool currentStatus = data[y][x];
// 周囲8マスに存在する生きたセルの数
int activeCellCount = getCount(x, y);
// 誕生:死んでいるセルに隣接する生きたセルがちょうど3つあれば、次の世代が誕生する。
if (!currentStatus && activeCellCount == 3) next[y][x] = true;
// 生存:生きているセルに隣接する生きたセルが2つか3つならば、次の世代でも生存する。
if (currentStatus && (activeCellCount == 2 || activeCellCount == 3)) {
next[y][x] = true;
}
// 過疎:生きているセルに隣接する生きたセルが1つ以下ならば、過疎により死滅する。
// 過密:生きているセルに隣接する生きたセルが4つ以上ならば、過密により死滅する。
if (currentStatus && (activeCellCount <= 1 && activeCellCount >= 4)) {
next[y][x] = false;
}
}
}
// 次世代に更新する
data = next;
}
int getCount(int x, int y) {
int count = 0;
// 8つの近傍セルをループして生きたセルを数える
for (auto &&dx : {-1, 0, 1}) {
for (auto &&dy : {-1, 0, 1}) {
// 自身を無視
if (dx == 0 && dy == 0) continue;
// 範囲外の判定
int nx = x + dx;
int ny = y + dy;
if (nx < 0 || nx >= width) continue;
if (ny < 0 || ny >= height) continue;
// 生きたセルを数える
count += data[ny][nx] ? 1 : 0;
}
}
return count;
}
void display() {
std::system("cls");
for (int y = 0; y < height; y++) {
for (int x = 0; x < width; x++) {
if (data[y][x]) {
cout << "■";
} else {
cout << "□";
}
}
cout << endl;
}
}
};
int main() {
LifeGame game(20, 15);
// テストデータ(ヒキガエル)
game.data[3][3] = true;
game.data[3][4] = true;
game.data[3][5] = true;
game.data[4][4] = true;
game.data[4][5] = true;
game.data[4][6] = true;
// テストデータ(ブリンカー)
game.data[10][10] = true;
game.data[11][10] = true;
game.data[12][10] = true;
// 開始
game.start();
return 0;
}実行結果
実行したらこんな感じで動きます。
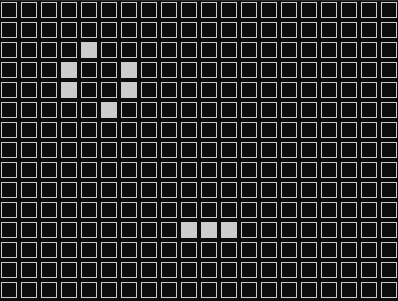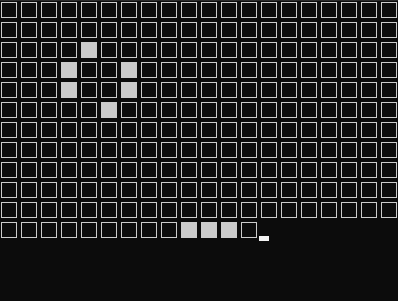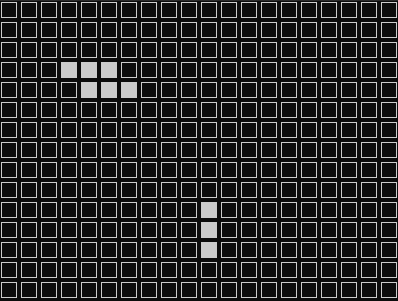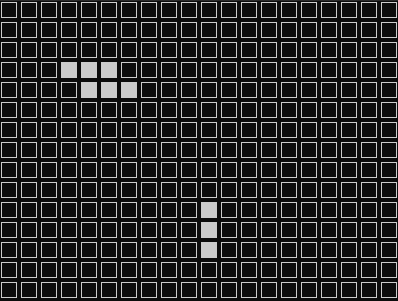
とりあえず動いていそうです。
以上。
![[C++] ライフゲームを実装する](https://webbibouroku.com/wp-content/uploads/cpp_logo-730x410.png)



コメントを書く